shen WANG


Hi!👋 I am currently a FIRST SECOND 3rd year Ph.D. student in the Department of Computing at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, under the supervision of Dr. Lei Yang. Previously, I received my B.E. from Harbin Institute of Technology. My main research interests are centered around on wireless spatial intelligence and 3D vision.
Hi!👋 I am currently a FIRST SECOND 3rd year Ph.D. student in the Department of Computing at the Hong Kong Polytechnic University, under the supervision of Dr. Lei Yang. Previously, I received my B.E. from Harbin Institute of Technology. My main research interests are centered around on wireless spatial intelligence and 3D vision.

Education
-
The Hong Kong Polytechnic University
Ph.D. Student in Computer Science 2023 - 2027(expected)
-

Harbin Institute of Technology
B.E. in Computer Science and Technology 2019 - 2023
Honors & Awards
- Ministry of Education of China - HUAWEI“Future Star" 2022
- First Grade Scholarship of H.I.T 2021
- Outstanding Student of H.I.T 2020
Selected Publications (view all )
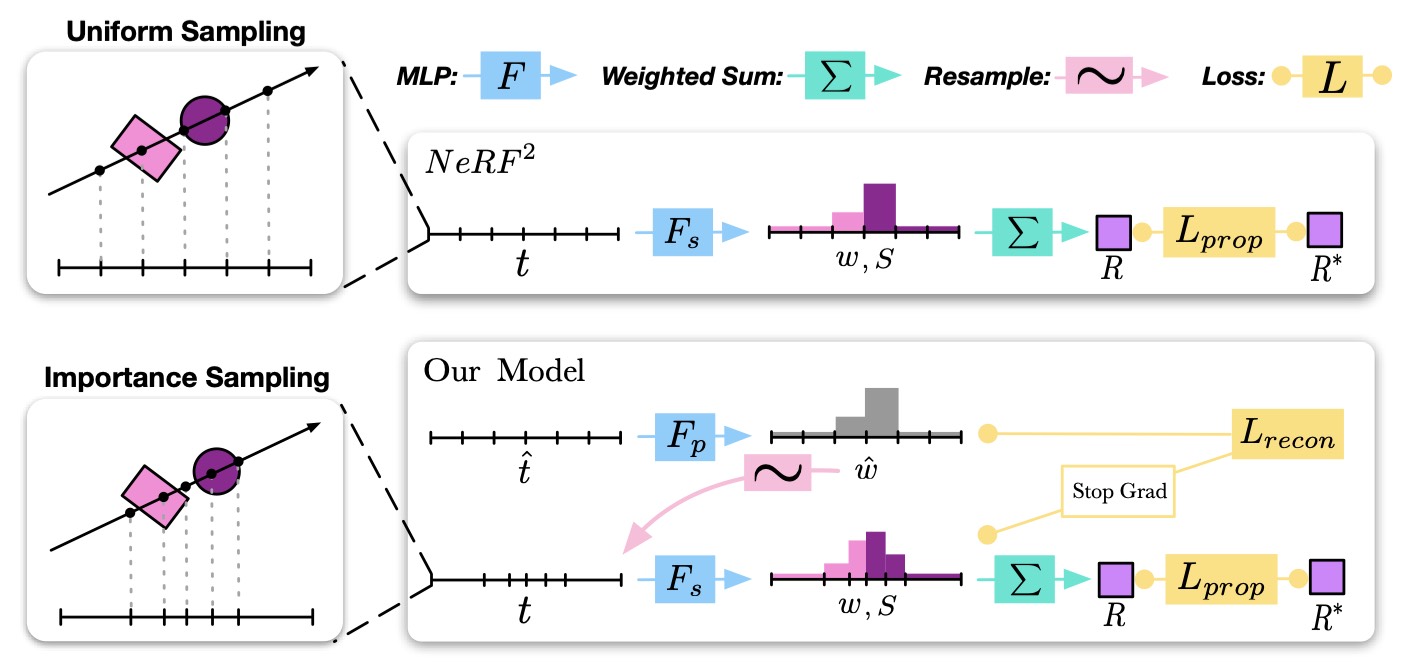
SIGN-RF: Self-Adaptive Neural Fields for Scalable Urban Radio Reconstruction
Shen Wang, Guosheng Wang, Junyang Liu, Donghui Dai, Lei Yang
IEEE INFOCOM (CCF-A) 2026
Accurate modeling of urban-scale wireless channels is critical for the next-generation 5G/6G communication systems. Conventional approaches—both deterministic and statistical are inherently limited by a trade-off between accuracy and computational efficiency. While recent advances in neural radiance fields (NeRF^2) have shown promise for indoor channel prediction, their extension to urban-scale environments remains infeasible due to the need for large-scale labeled measurements and the substantial computational overhead required for high-resolution radiance field representations. To address these challenges, we propose SIGN-RF, a self-adaptive neural field framework for urban-scale radio reconstruction.
SIGN-RF: Self-Adaptive Neural Fields for Scalable Urban Radio Reconstruction
Shen Wang, Guosheng Wang, Junyang Liu, Donghui Dai, Lei Yang
IEEE INFOCOM (CCF-A) 2026
Accurate modeling of urban-scale wireless channels is critical for the next-generation 5G/6G communication systems. Conventional approaches—both deterministic and statistical are inherently limited by a trade-off between accuracy and computational efficiency. While recent advances in neural radiance fields (NeRF^2) have shown promise for indoor channel prediction, their extension to urban-scale environments remains infeasible due to the need for large-scale labeled measurements and the substantial computational overhead required for high-resolution radiance field representations. To address these challenges, we propose SIGN-RF, a self-adaptive neural field framework for urban-scale radio reconstruction.
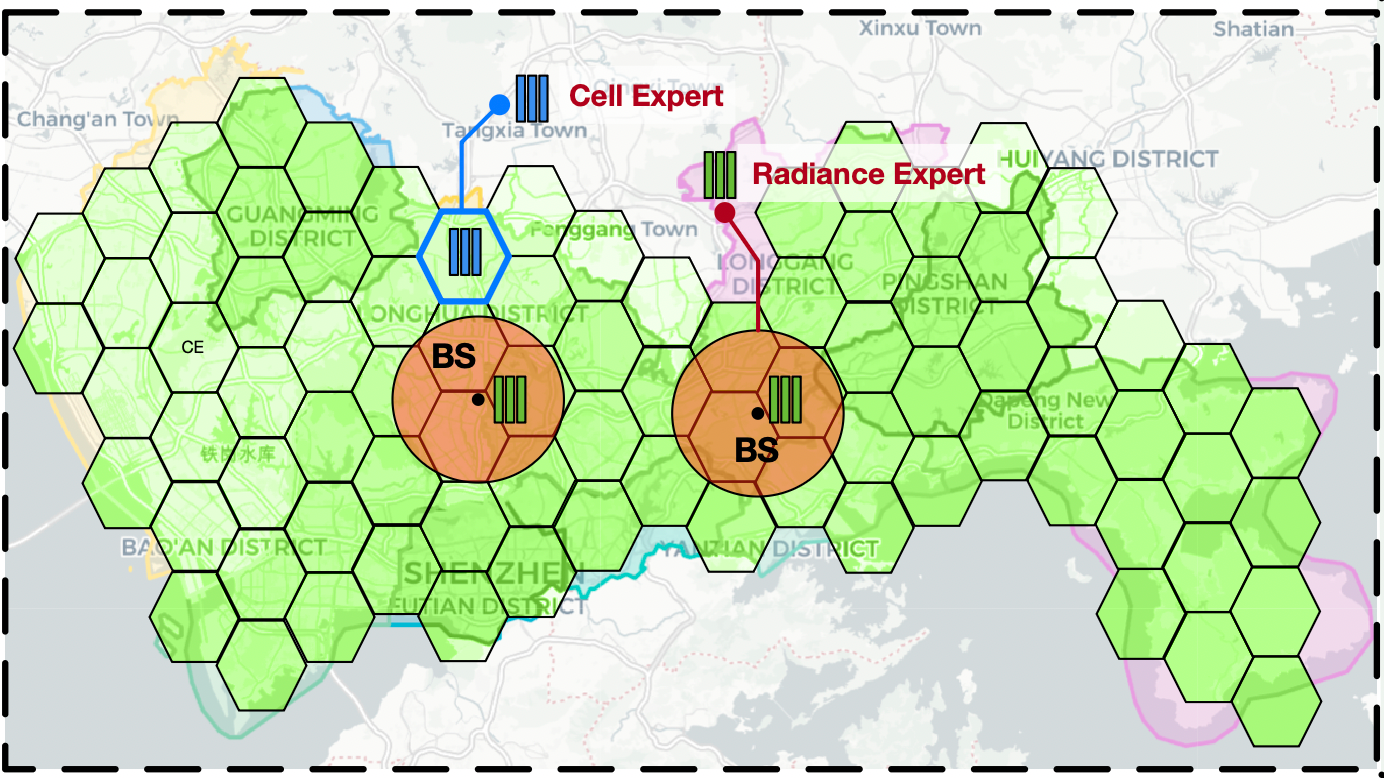
City-Scale Radiance-Field Reconstruction via Mixture of Radio Experts
Shen Wang, Guosheng Wang, Donghui Dai, Lei Yang
ACM MobiCom (CCF-A) 2026
Accurately modeling the radiance field of 5G signals in urban environments is essential for reliable network operation and scalable planning of next-generation wireless systems. Recent advances in neural radiance fields NeRF^2 have shown great success in capturing the spatially continuous behavior of radio propagation. However, existing NeRF^2 frameworks remain limited to small-scale scenes, suffering from severe accuracy degradation and prohibitive computational costs when extended to city-scale deployments. In this work, we present Mixture of Radio Experts (MoRE), a mixture-of-experts architecture designed for city-scale 5G radiance field reconstruction.
City-Scale Radiance-Field Reconstruction via Mixture of Radio Experts
Shen Wang, Guosheng Wang, Donghui Dai, Lei Yang
ACM MobiCom (CCF-A) 2026
Accurately modeling the radiance field of 5G signals in urban environments is essential for reliable network operation and scalable planning of next-generation wireless systems. Recent advances in neural radiance fields NeRF^2 have shown great success in capturing the spatially continuous behavior of radio propagation. However, existing NeRF^2 frameworks remain limited to small-scale scenes, suffering from severe accuracy degradation and prohibitive computational costs when extended to city-scale deployments. In this work, we present Mixture of Radio Experts (MoRE), a mixture-of-experts architecture designed for city-scale 5G radiance field reconstruction.

Mirror Never Lies: Unveiling Reflective Privacy Risks in Glass-laden Short Videos
Shen Wang, Xiaopeng Zhao, Donghui Dai, Lei Yang
ACM MobiCom (CCF-A) 2024
In the era of ubiquitous short-video sharing, an overlooked yet significant privacy risk has arisen, the accidental disclosure of confidential information through reflective surfaces, such as mirrors, glass, or even polished metal. Such reflections can inadvertently disclose sensitive personal details to a broad audience without the awareness of content creators. Our examination of 100 top-rated TikTok short videos reveals that, on average, 37.2% of frames in each video feature identifiable reflective surfaces, posing potential privacy risks. In this work, we introduce a framework designed to scrutinize reflective privacy risks in glass-laden short videos. At the heart of the framework is the development of a reflection-specific neural radiance field, termed RP-NeRF, which enables reflection-aware ray tracing for precise extraction and reconstruction of the reflective scenes from the surfaces they appear on.
Mirror Never Lies: Unveiling Reflective Privacy Risks in Glass-laden Short Videos
Shen Wang, Xiaopeng Zhao, Donghui Dai, Lei Yang
ACM MobiCom (CCF-A) 2024
In the era of ubiquitous short-video sharing, an overlooked yet significant privacy risk has arisen, the accidental disclosure of confidential information through reflective surfaces, such as mirrors, glass, or even polished metal. Such reflections can inadvertently disclose sensitive personal details to a broad audience without the awareness of content creators. Our examination of 100 top-rated TikTok short videos reveals that, on average, 37.2% of frames in each video feature identifiable reflective surfaces, posing potential privacy risks. In this work, we introduce a framework designed to scrutinize reflective privacy risks in glass-laden short videos. At the heart of the framework is the development of a reflection-specific neural radiance field, termed RP-NeRF, which enables reflection-aware ray tracing for precise extraction and reconstruction of the reflective scenes from the surfaces they appear on.
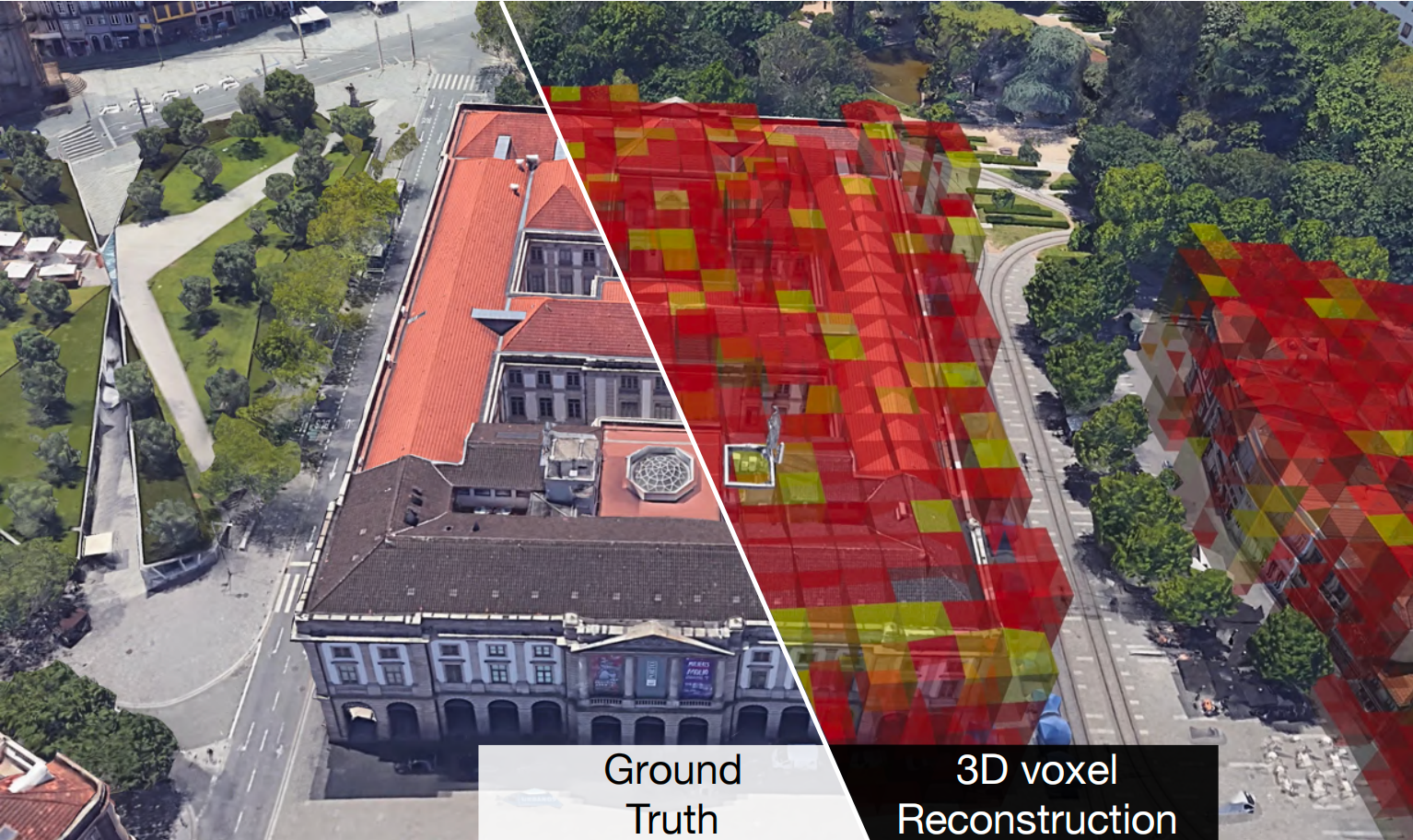
Crowdsourced Geospatial Intelligence: Constructing 3D Urban Maps with Satellitic Radiance Fields
Xiaopeng Zhao*, Shen Wang*, Zhenlin An, Lei Yang(* equal contribution)
ACM IMWUT/UbiComp (CCF-A) 2024
In urban planning and research, 3D city maps are crucial for activities such as cellular network design, urban development, and climate research. Traditionally, creating these models has involved costly techniques like manual 3D mapping, interpretation of satellite or aerial images, or the use of sophisticated depth-sensing equipment. In this work, we propose a novel approach to develop 3D urban maps by examining the influence of urban structures on satellite signals, using GPS records crowdsourced from hundreds of smartphones during everyday user movements. We introduce the concept of satellitic radiance fields (SaRF), a novel neural scene representation technique designed to capture the distribution of GPS signals in urban settings. SaRF employs a sparse voxel octree framework to depict voxel-centric implicit fields, capturing physical properties like the density of each voxel. This model is progressively refined using a differentiable ray-marching process, ultimately leading to the reconstruction of 3D urban maps.
Crowdsourced Geospatial Intelligence: Constructing 3D Urban Maps with Satellitic Radiance Fields
Xiaopeng Zhao*, Shen Wang*, Zhenlin An, Lei Yang(* equal contribution)
ACM IMWUT/UbiComp (CCF-A) 2024
In urban planning and research, 3D city maps are crucial for activities such as cellular network design, urban development, and climate research. Traditionally, creating these models has involved costly techniques like manual 3D mapping, interpretation of satellite or aerial images, or the use of sophisticated depth-sensing equipment. In this work, we propose a novel approach to develop 3D urban maps by examining the influence of urban structures on satellite signals, using GPS records crowdsourced from hundreds of smartphones during everyday user movements. We introduce the concept of satellitic radiance fields (SaRF), a novel neural scene representation technique designed to capture the distribution of GPS signals in urban settings. SaRF employs a sparse voxel octree framework to depict voxel-centric implicit fields, capturing physical properties like the density of each voxel. This model is progressively refined using a differentiable ray-marching process, ultimately leading to the reconstruction of 3D urban maps.
